1.3: Square and Cube Roots of Real Numbers
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
Learning Objectives
- Calculate the exact and approximate value of the square root of a real number.
- Calculate the exact and approximate value of the cube root of a real number.
- Simplify the square and cube root of a real number.
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem.
The Definition of Square and Cube Roots
A square root74 of a number is a number that when multiplied by itself yields the original number. For example,
Zero is the only real number with exactly one square root.
If the radicand77, the number inside the radical sign, is nonzero and can be factored as the square of another nonzero number, then the square root of the number is apparent. In this case, we have the following property:
It is important to point out that
This distinction will be carefully considered later in the course.
Example
Find the square root:
Solution
Example
Find the negative square root:
Solution
The radicand may not always be a perfect square. If a positive integer is not a perfect square, then its square root will be irrational. Consider
With this we conclude that
Next, consider the square root of a negative number. To determine the square root of
However, any real number squared always results in a positive number,
The square root of a negative number is currently left undefined. Try calculating
A cube root78 of a number is a number that when multiplied by itself three times yields the original number. Furthermore, we denote a cube root using the symbol
The product of three equal factors will be positive if the factor is positive, and negative if the factor is negative. For this reason, any real number will have only one real cube root. Hence the technicalities associated with the principal root do not apply. For example,
In general, given any real number
When simplifying cube roots, look for factors that are perfect cubes.
Example
Find the cube root:
Solution
Example
Find the cube root:
Solution
It may be the case that the radicand is not a perfect cube. If this is the case, then its cube root will be irrational. For example,
Therefore, we have
We will extend these ideas using any integer as an index later in this course. It is important to point out that a square root has index
Simplifying Square and Cube Roots
It will not always be the case that the radicand is a perfect square. If not, we use the following two properties to simplify the expression. Given real numbers
A simplified radical82 is one where the radicand does not consist of any factors that can be written as perfect powers of the index. Given a square root, the idea is to identify the largest square factor of the radicand and then apply the property shown above. As an example, to simplify
The number
As a check, calculate
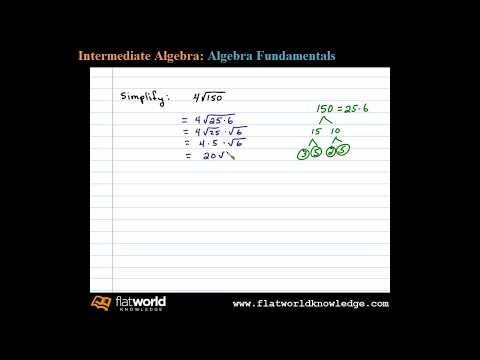
Example
Simplify:
Solution
Begin by finding the largest perfect square factor of
Therefore,
Answer
Example
Simplify:
Solution
We begin by finding the prime factorizations of both
Therefore,
Answer
Example
Simplify
Solution
Answer
Exercise
Simplify
- Answer
-
A cube root is simplified if it does not contain any factors that can be written as perfect cubes. The idea is to identify the largest cube factor of the radicand and then apply the product or quotient rule for radicals. As an example, to simplify
Example
Simplify
Solution
Begin by finding the largest perfect cube factor of
Therefore,
Answer
Example
Simplify:
Solution
Answer
Exercise
Simplify
- Answer
-
www.youtube.com/v/oEzfrahfb0A
Consider the following two calculations,
Notice that it does not matter if we apply the exponent first or the square root first. This is true for any positive real number. We have the following,
Example
Simplify:
Solution
Apply the fact that
Pythagorean Theorem
A right triangle83 is a triangle where one of the angles measures

Example
Calculate the diagonal of a square with sides measuring
Solution
The diagonal of a square will form an isosceles right triangle where the two equal legs measure

We can use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of the hypotenuse.
Answer:
The Pythagorean theorem actually states that having side lengths satisfying the property
Example
Determine whether or not a triangle with legs
Solution
If the legs satisfy the condition
Answer: Yes, the described triangle is a right triangle.
Key Takeaways
- The square root of a number is a number that when squared results in the original number. The principal square root of a positive real number is the positive square root. The square root of a negative number is currently left undefined.
- When simplifying the square root of a number, look for perfect square factors of the radicand. Apply the product or quotient rule for radicals and then simplify.
- The cube root of a number is a number that when cubed results in the original number. Every real number has only one real cube root.
- When simplifying cube roots, look for perfect cube factors of the radicand. Apply the product or quotient rule for radicals and then simplify.
- The Pythagorean theorem gives us a necessary and sufficient condition of right triangles:
Exercise
- Answer
-
1.
3.
5.
7.
9. Not a real number.
11.
13.
15.
17.
19.
21.
23.
25.
27.
29.
31.
33.
35.
37.
Exercise
Use a calculator to approximate to the nearest hundredth.
- Determine the set consisting of the squares of the first twelve positive integers.
- Determine the set consisting of the cubes of the first twelve positive integers.
- Answer
-
1.
3.
5.
7.
9.
11.
13.
Exercise
Simplify.
- Answer
-
1.
3.
5.
7.
9.
11. Not a real number.
13.
15.
17.
19.
21.
23. 64
25. 2
Exercise
- If the two legs of a right triangle measure
- If the two legs of a right triangle measure
- If the two equal legs of an isosceles right triangle measure
- If the two equal legs of an isosceles right triangle measure
- Calculate the diagonal of a square with sides measuring
- Calculate the diagonal of a square with sides measuring
- Calculate the diagonal of a square with sides measuring
- Calculate the diagonal of a square with sides measuring
- Calculate the length of the diagonal of a rectangle with dimensions
- Calculate the length of the diagonal of a rectangle with dimensions
- Calculate the length of the diagonal of a rectangle with dimensions
- Calculate the length of the diagonal of a rectangle with dimensions
- To ensure that a newly built gate is square, the measured diagonal must match the distance calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. If the gate measures
- If a doorframe measures
- Answer
-
1.
3.
5.
7.
9.
11.
13. The diagonal must measure approximately
Exercise
Determine whether or not the given triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c is a right triangle or not.
- Answer
-
1. Not a right triangle.
3. Right triangle.
5. Right triangle.
7. Right triangle.
Exercise
- What does your calculator say after taking the square root of a negative number? Share your results on the discussion board and explain why it says that.
- Research and discuss the history of the Pythagorean theorem.
- Research and discuss the history of the square root.
- Discuss the importance of the principal square root. Why is it that the same issue does not come up with cube roots? Provide some examples with your explanation.
- Answer
-
1. Answer may vary
3. Answer may vary
Footnotes
74That number that when multiplied by itself yields the original number.
75The symbol
76The non-negative square root.
77The number within a radical.
78The number that when multiplied by itself three times yields the original number, denoted by
79The positive integer
80Given real numbers
81Given real numbers
82A radical where the radicand does not consist of any factors that can be written as perfect powers of the index.
83A triangle with an angle that measures
84The longest side of a right triangle; it will always be the side opposite the right angle.
85The sides of a right triangle that are not the hypotenuse.
86The hypotenuse of any right triangle is equal to the square root of the sum of the squares of the lengths of the triangle’s legs.