8.E: Conic Sections (Exercises)
- Page ID
- 6287
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Calculate the distance and midpoint between the given two points.
- \((0,2)\) and \((-4,-1)\)
- \((6,0)\) and \((-2,-6)\)
- \((-2,4)\) and \((-6,-8)\)
- \(\left(\frac{1}{2},-1\right)\) and \(\left(\frac{5}{2},-\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
- \((0,-3 \sqrt{2})\) and \((\sqrt{5},-4 \sqrt{2})\)
- \((-5 \sqrt{3}, \sqrt{6})\) and \((-3 \sqrt{3}, \sqrt{6})\)
- Answer
-
1. Distance: \(5\) units; midpoint: \(\left(-2, \frac{1}{2}\right)\)
3. Distance: \(4\sqrt{10}\) units; midpoint: \((-4,-2)\)
5. Distance: \(\sqrt{7}\) units; midpoint: \(\left(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2},-\frac{7 \sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Determine the area of a circle whose diameter is defined by the given two points.
- \((-3,3)\) and \((3,-3)\)
- \((-2,-9)\) and \((-10,-15)\)
- \(\left(\frac{2}{3},-\frac{1}{2}\right)\) and \(\left(-\frac{1}{3}, \frac{3}{2}\right)\)
- \((2 \sqrt{5},-2 \sqrt{2})\) and \((0,-4 \sqrt{2})\)
- Answer
-
1. \(18\pi\) square units
3. \(\frac{5 \pi}{4}\) square units
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Rewrite in standard form and give the vertex.
- \(y=x^{2}-10 x+33\)
- \(y=2 x^{2}-4 x-1\)
- \(y=x^{2}-3 x-1\)
- \(y=-x^{2}-x-2\)
- \(x=y^{2}+10 y+10\)
- \(x=3 y^{2}+12 y+7\)
- \(x=-y^{2}+8 y-3\)
- \(x=5 y^{2}-5 y+2\)
- Answer
-
1. \(y=(x-5)^{2}+8 ;\) vertex: \((5,8)\)
3. \(y=\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^{2}-\frac{13}{4} ;\) vertex: \(\left(\frac{3}{2},-\frac{13}{4}\right)\)
5. \(x=(y+5)^{2}-15 ;\) vertex: \((-15,-5)\)
7. \(x=-(y-4)^{2}+13 ;\) vertex: \((13,4)\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Rewrite in standard form and graph. Be sure to find the vertex and all intercepts.
- \(y=x^{2}-20 x+75\)
- \(y=-x^{2}-10 x+75\)
- \(y=-2 x^{2}-12 x-24\)
- \(y=4 x^{2}+4 x+6\)
- \(x=y^{2}-10 y+16\)
- \(x=-y^{2}+4 y+12\)
- \(x=-4 y^{2}+12 y\)
- \(x=9 y^{2}+18 y+12\)
- \(x=-4 y^{2}+4 y+2\)
- \(x=-y^{2}-5 y+2\)
- Answer
-
1. \(y=(x-10)^{2}-25\);

Figure 8.E.1 3. \(y=-2(x+3)^{2}-6\);

Figure 8.E.2 5. \(x=(y-5)^{2}-9\);

Figure 8.E.3 7. \(x=-4\left(y-\frac{3}{2}\right)^{2}+9\);

Figure 8.E.4 9. \(x=-4\left(y-\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+3\);

Figure 8.E.5
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Determine the center and radius given the equation of a circle in standard form.
- \((x-6)^{2}+y^{2}=9\)
- \((x+8)^{2}+(y-10)^{2}=1\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}=5\)
- \(\left(x-\frac{3}{8}\right)^{2}+\left(y+\frac{5}{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
- Answer
-
1. Center: \((6,0) ;\) radius: \(r=3\)
3. Center: \((0,0) ;\) radius: \(r=\sqrt{5}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Determine standard form for the equation of the circle:
- Center \((-7,2)\) with radius \(r=10\)
- Center \(\left(\frac{1}{3},-1\right)\) with radius \(r=\frac{2}{3}\)
- Center \((0,-5)\) with radius \(r=2 \sqrt{7}\)
- Center \((1,0)\) with radius \(r=\frac{5 \sqrt{3}}{2}\)
- Circle whose diameter is defined by \((-4,10)\) and \((-2,8)\)
- Circle whose diameter is defined by \((3,-6)\) and \((0,-4)\)
- Answer
-
1. \((x+7)^{2}+(y-2)^{2}=100\)
3. \(x^{2}+(y+5)^{2}=28\)
5. \((x+3)^{2}+(y-9)^{2}=2\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\)
Find the \(x\)- and \(y\)-intercepts.
- \((x-3)^{2}+(y+5)^{2}=16\)
- \((x+5)^{2}+(y-1)^{2}=4\)
- \(x^{2}+(y-2)^{2}=20\)
- \((x-3)^{2}+(y+3)^{2}=8\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}-12 y+27=0\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}-4 x+2 y+1=0\)
- Answer
-
1. \(x\)-intercepts: none; \(y\)-intercepts: \((0,-5 \pm \sqrt{7})\)
3. \(x\)-intercepts: \((\pm 4,0)\); \(y\)-intercepts: \((0,2 \pm 2 \sqrt{5})\)
5. \(x\)-intercepts: none; \(y\)-intercepts: \((0,3),(0,9)\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8}\)
Graph.
- \((x+8)^{2}+(y-6)^{2}=4\)
- \((x-20)^{2}+\left(y+\frac{15}{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{225}{4}\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}=24\)
- \((x-1)^{2}+y^{2}=\frac{1}{4}\)
- \(x^{2}+(y-7)^{2}=27\)
- \((x+1)^{2}+(y-1)^{2}=2\)
- Answer
-
1.

Figure 8.E.6 3.

Figure 8.E.7 5.

Figure 8.E.8
Exercise \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Rewrite in standard form and graph.
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}-6 x+4 y-3=0\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}+8 x-10 y+16=0\)
- \(2 x^{2}+2 y^{2}-2 x-6 y-3=0\)
- \(4 x^{2}+4 y^{2}+8 y+1=0\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}-5 x+y-\frac{1}{2}=0\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}+12 x-8 y=0\)
- Answer
-
1. \((x-3)^{2}+(y+2)^{2}=16\);

Figure 8.E.9 3. \(\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+\left(y-\frac{3}{2}\right)^{2}=4\);

Figure 8.E.10 5. \(\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^{2}+\left(y+\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}=7\);

Figure 8.E.11
Exercise \(\PageIndex{10}\)
Given the equation of an ellipse in standard form, determine its center, orientation, major radius, and minor radius.
- \(\frac{(x+12)^{2}}{16}+\frac{(y-10)^{2}}{4}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x+3)^{2}}{3}+\frac{y^{2}}{25}=1\)
- \(x^{2}+\frac{(y-5)^{2}}{12}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x-8)^{2}}{5}+\frac{(y+8)}{18}=1\)
- Answer
-
1. Center: \((−12, 10)\); orientation: horizontal; major radius: \(4\) units; minor radius: \(2\) units
3. Center: \((0, 5)\); orientation: vertical; major radius: \(2\sqrt{3}\) units; minor radius: \(1\) unit
Exercise \(\PageIndex{11}\)
Determine the standard form for the equation of the ellipse given the following information.
- Center \((0,-4)\) with \(a=3\) and \(b=4\)
- Center \((3,8)\) with \(a=1\) and \(b=\sqrt{7}\)
- Center \((0,0)\) with \(a=5\) and \(b=\sqrt{2}\)
- Center \((-10,-30)\) with \(a=10\) and \(b=1\)
- Answer
-
1. \(\frac{x^{2}}{9}+\frac{(y+4)^{2}}{16}=1\)
3. \(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{2}=1\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{12}\)
Find the \(x\)- and \(y\)-intercepts.
- \(\frac{(x+2)^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{2}+\frac{(y+1)^{2}}{3}=1\)
- \(5 x^{2}+2 y^{2}=20\)
- \(5(x-3)^{2}+6 y^{2}=120\)
- Answer
-
1. \(x\) -intercepts: \((-4,0),(0,0) ; y\) -intercepts: \((0,0)\)
3. \(x\) -intercepts: \((\pm 2,0) ; y\) -intercepts: \((0, \pm \sqrt{10})\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Graph.
- \(\frac{(x-10)^{2}}{25}+\frac{(y+5)^{2}}{4}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x+6)^{2}}{9}+\frac{(y-8)^{2}}{36}=1\)
- \(\frac{\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^{2}}{4}+\left(y-\frac{7}{2}\right)^{2}=1\)
- \(\left(x-\frac{2}{3}\right)^{2}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}=1\)
- \(\frac{x^{2}}{2}+\frac{y^{2}}{5}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x+2)^{2}}{8}+\frac{(y-3)^{2}}{12}=1\)
- Answer
-
1.

Figure 8.E.12 3.

Figure 8.E.13 5.

Figure 8.E.14
Exercise \(\PageIndex{14}\)
Rewrite in standard form and graph.
- \(4 x^{2}+9 y^{2}-8 x+90 y+193=0\)
- \(9 x^{2}+4 y^{2}+108 x-80 y+580=0\)
- \(x^{2}+9 y^{2}+6 x+108 y+324=0\)
- \(25 x^{2}+y^{2}-350 x-8 y+1,216=0\)
- \(8 x^{2}+12 y^{2}-16 x-36 y-13=0\)
- \(10 x^{2}+2 y^{2}-50 x+14 y+7=0\)
- Answer
-
1. \(\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{9}+\frac{(y+5)^{2}}{4}=1\);

Figure 8.E.15 3. \(\frac{(x+3)^{2}}{9}+(y+6)^{2}=1\);

Figure 8.E.16 5. \(\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{6}+\frac{\left(y-\frac{3}{2}\right)^{2}}{4}=1\);

Figure 8.E.17
Exercise \(\PageIndex{15}\)
Given the equation of a hyperbola in standard form, determine its center, which way the graph opens, and the vertices.
- \(\frac{(x-10)^{2}}{4}-\frac{(y+5)^{2}}{16}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x+7)^{2}}{2}-\frac{(y-8)^{2}}{8}=1\)
- \(\frac{(y-20)^{2}}{3}-(x-15)^{2}=1\)
- \(3 y^{2}-12(x-1)^{2}=36\)
- Answer
-
1. Center: \((10,-5)\); opens left and right; vertices: \((8,-5),(12,-5)\)
3. Center: \((15,20)\); opens upward and downward; vertices: \((15,20-\sqrt{3}),(15,20+\sqrt{3})\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{16}\)
Determine the standard form for the equation of the hyperbola.
- Center \((-25,10), a=3, b=\sqrt{5},\) opens up and down.
- Center \((9,-12), a=5 \sqrt{3}, b=7,\) opens left and right.
- Center \((-4,0), a=1, b=6,\) opens left and right.
- Center \((-2,-3), a=10 \sqrt{2}, b=2 \sqrt{3},\) opens up and down.
- Answer
-
1. \(\frac{(y-10)^{2}}{5}-\frac{(x+25)^{2}}{9}=1\)
3. \((x+4)^{2}-\frac{y^{2}}{36}=1\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{17}\)
Find the \(x\)- and \(y\)-intercepts.
- \(\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{4}-\frac{(y+3)^{2}}{9}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x+4)^{2}}{8}-\frac{(y-2)^{2}}{12}=1\)
- \(4(y-2)^{2}-x^{2}=16\)
- \(6(y+1)^{2}-3(x-1)^{2}=18\)
- Answer
-
1. \(x\) -intercepts: \((1 \pm 2 \sqrt{2}, 0) ; y\) -intercepts: none
3. \(x\) -intercepts: \((0,0) ; y\) -intercepts: \((0,0),(0,4)\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{18}\)
Graph.
- \(\frac{(x-10)^{2}}{25}-\frac{(y+5)^{2}}{100}=1\)
- \(\frac{(x-4)^{2}}{4}-\frac{(y-8)^{2}}{16}=1\)
- \(\frac{(y-3)^{2}}{9}-\frac{(x-6)^{2}}{81}=1\)
- \(\frac{(y+1)^{2}}{4}-\frac{(x+1)^{2}}{25}=1\)
- \(\frac{y^{2}}{27}-\frac{(x-3)^{2}}{9}=1\)
- \(\frac{x^{2}}{2}-\frac{y^{2}}{3}=1\)
- Answer
-
1.

Figure 8.E.18 3.

Figure 8.E.19 5.

Figure 8.E.20
Exercise \(\PageIndex{19}\)
Rewrite in standard form and graph.
- \(4 x^{2}-9 y^{2}-8 x-90 y-257=0\)
- \(9 x^{2}-y^{2}-108 x+16 y+224=0\)
- \(25 y^{2}-2 x^{2}-100 y+50=0\)
- \(3 y^{2}-x^{2}-2 x-10=0\)
- \(8 y^{2}-12 x^{2}+24 y-12 x-33=0\)
- \(4 y^{2}-4 x^{2}-16 y-28 x-37=0\)
- Answer
-
1. \(\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{9}-\frac{(y+5)^{2}}{4}=1\);

Figure 8.E.21 3. \(\frac{(y-2)^{2}}{2}-\frac{x^{2}}{25}=1\);

Figure 8.E.22 5. \(\frac{\left(y+\frac{3}{2}\right)^{2}}{6}-\frac{\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}}{4}=1\)

Figure 8.E.23
Exercise \(\PageIndex{20}\)
Identify the conic sections and rewrite in standard form.
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}-2 x-8 y+16=0\)
- \(x^{2}+2 y^{2}+4 x-24 y+74=0\)
- \(x^{2}-y^{2}-6 x-4 y+3=0\)
- \(x^{2}+y-10 x+22=0\)
- \(x^{2}+12 y^{2}-12 x+24=0\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}+10 y+22=0\)
- \(4 y^{2}-20 x^{2}+16 y+20 x-9=0\)
- \(16 x-16 y^{2}+24 y-25=0\)
- \(9 x^{2}-9 y^{2}-6 x-18 y-17=0\)
- \(4 x^{2}+4 y^{2}+4 x-8 y+1=0\)
- Answer
-
1. Circle;\((x-1)^{2}+(y-4)^{2}=1\)
3. Hyperbola; \(\frac{(x-3)^{2}}{2}-\frac{(y+2)^{2}}{2}=1\)
5. Ellipse; \(\frac{(x-6)^{2}}{12}+y^{2}=1\)
7. Hyperbola; \(\frac{(y+2)^{2}}{5}-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}=1\)
9. Hyperbola; \(\left(x-\frac{1}{3}\right)^{2}-(y+1)^{2}=1\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{21}\)
Given the graph, write the equation in general form.
1.

2.

3.

4.

5.

6.

- Answer
-
1. \(x^{2}+y^{2}+18 x-6 y+9=0\)
3. \(9 x^{2}-y^{2}+72 x-12 y+72=0\)
5. \(9 x^{2}+64 y^{2}+54 x-495=0\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{22}\)
Solve.
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{x^{2}+y^{2}=8} \\ {x-y=4}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{x^{2}+y^{2}=1} \\ {x+2 y=1}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{x^{2}+3 y^{2}=4} \\ {2 x-y=1}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{2 x^{2}+y^{2}=5} \\ {x+y=3}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{3 x^{2}-2 y^{2}=1} \\ {x-y=2}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{x^{2}-3 y^{2}=10} \\ {x-2 y=1}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{2 x^{2}+y^{2}=11} \\ {4 x+y^{2}=5}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{x^{2}+4 y^{2}=1} \\ {2 x^{2}+4 y=5}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{5 x^{2}-y^{2}=10} \\ {x^{2}+y=2}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{2 x^{2}+y^{2}=1} \\ {2 x-4 y^{2}=-3}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{x^{2}+4 y^{2}=10} \\ {x y=2}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{y+x^{2}=0} \\ {x y-8=0}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=10} \\ {\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{y}=6}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=1} \\ {y-x=2}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{x-2 y^{2}=3} \\ {y=\sqrt{x-4}}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{(x-1)^{2}+y^{2}=1} \\ {y-\sqrt{x}=0}\end{array}\right.\)
- Answer
-
1. \((2,-2)\)
3. \(\left(-\frac{1}{13},-\frac{15}{13}\right),(1,1)\)
5. \((-9,-11),(1,-1)\)
7. \((-1,-3),(-1,3)\)
9. \((-\sqrt{2}, 0),(\sqrt{2}, 0),(-\sqrt{7},-5),(\sqrt{7},-5)\)
11. \((\sqrt{2}, \sqrt{2}) \cdot(-\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{2}) \cdot\left(2 \sqrt{2}, \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right) \cdot\left(-2 \sqrt{2},-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\)
13. \(\left(\frac{1}{8}, \frac{1}{2}\right)\)
15. \((5,1)\)
Sample Exam
Exercise \(\PageIndex{23}\)
- Given two points \((-4,-6)\) and \((2,-8)\):
- Calculate the distance between them.
- Find the midpoint between them.
- Determine the area of a circle whose diameter is defined by the points \((4, −3)\) and \((−1, 2)\).
- Answer
-
1. (1) \(2\sqrt{10}\) units; (2) \((-1,-7)\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{24}\)
Rewrite in standard form and graph. Find the vertex and all intercepts if any.
- \(y=-x^{2}+6 x-5\)
- \(x=2 y^{2}+4 y-6\)
- \(x=-3 y^{2}+3 y+1\)
- Find the equation of a circle in standard form with center \((−6, 3)\) and radius \(2 \sqrt{5}\) units.
- Answer
-
1. \(y=-(x-3)^{2}+4\);

Figure 8.E.30 3. \(x=-3\left(y-\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+\frac{7}{4}\);
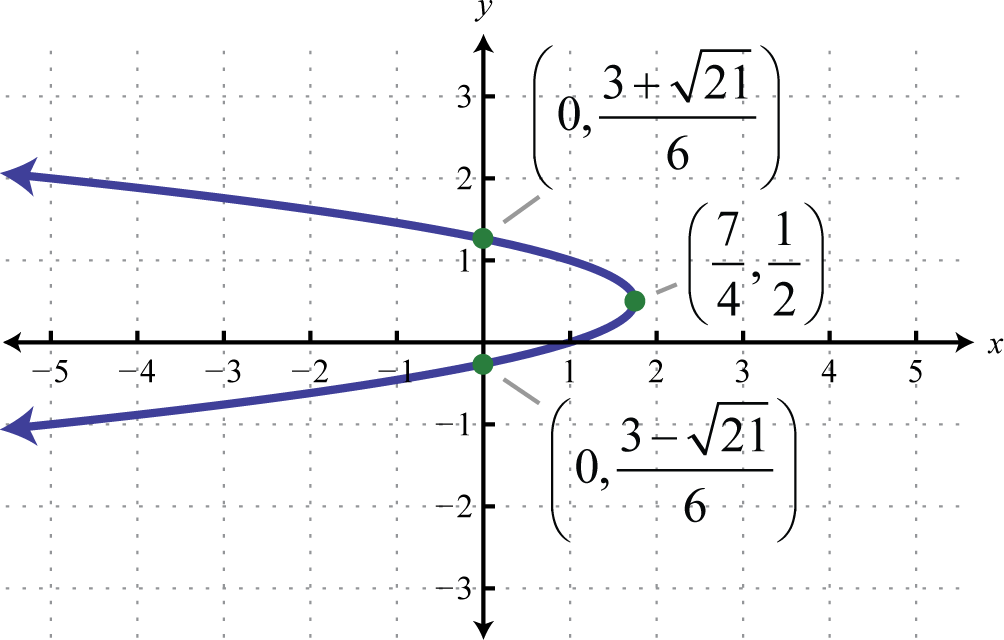
Figure 8.E.31
Exercise \(\PageIndex{25}\)
Sketch the graph of the conic section given its equation in standard form.
- \((x-4)^{2}+(y+1)^{2}=45\)
- \(\frac{(x+3)^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1\)
- \(\frac{y^{2}}{3}-\frac{x^{2}}{9}=1\)
- \(\frac{x^{2}}{16}-(y-2)^{2}=1\)
- Answer
-
1.

Figure 8.E.32 3.

Figure 8.E.33
Exercise \(\PageIndex{26}\)
Rewrite in standard form and graph.
- \(9 x^{2}+4 y^{2}-144 x+16 y+556=0\)
- \(x-y^{2}+6 y+7=0\)
- \(x^{2}+y^{2}+20 x-20 y+100=0\)
- \(4 y^{2}-x^{2}+40 y-30 x-225=0\)
- Answer
-
1. \(\frac{(x-8)^{2}}{4}+\frac{(y+2)^{2}}{9}=1\);

Figure 8.E.34 3. \((x+10)^{2}+(y-10)^{2}=100\);

Figure 8.E.35
Exercise \(\PageIndex{27}\)
Find the \(x\)- and \(y\)-intercepts.
- \(x=-2(y-4)^{2}+9\)
- \(\frac{(y-1)^{2}}{12}-(x+1)^{2}=1\)
- Answer
-
1. \(x\) -intercept: \((-23,0) ; y\) -intercepts: \(\left(0, \frac{8 \pm 3 \sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{28}\)
Solve.
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{x+y=2} \\ {y=-x^{2}+4}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}{y-x^{2}=-3} \\ {x^{2}+y^{2}=9}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{2 x-y=1} \\ {(x+1)^{2}+2 y^{2}=1}\end{array}\right.\)
- \(\left\{\begin{array}{c}{x^{2}+y^{2}=6} \\ {x y=3}\end{array}\right.\)
- Answer
-
1. \((-1,3),(2,0)\)
3. \(\emptyset\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{29}\)
- Find the equation of an ellipse in standard form with vertices \((−3, −5)\) and \((5, −5)\) and a minor radius \(2\) units in length.
- Find the equation of a hyperbola in standard form opening left and right with vertices \((\pm \sqrt{5}, 0)\) and a conjugate axis that measures \(10\) units.
- Given the graph of the ellipse, determine its equation in general form.

4. A rectangular deck has an area of \(80\) square feet and a perimeter that measures \(36\) feet. Find the dimensions of the deck.
5. The diagonal of a rectangle measures \(2\sqrt{13}\) centimeters and the perimeter measures \(20\) centimeters. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
- Answer
-
1. \(\frac{(x-1)^{2}}{16}+\frac{(y+5)^{2}}{4}=1\)
3. \(4 x^{2}+25 y^{2}-24 x-100 y+36=0\)
5. \(6\) centimeters by \(4\) centimeters


