3.1e: Exercises - Quadratic Functions
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
A: Concepts
Exercise 3.1e.A
1) Explain the advantage of writing a quadratic function in standard form.
2) How can the vertex of a parabola be used in solving real world problems?
3) Explain why the condition of a≠0 is imposed in the definition of the quadratic function.
4) What is another name for the standard form of a quadratic function?
5) What two algebraic methods can be used to find the horizontal intercepts of a quadratic function?
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
1. When written in that form, the vertex can be easily identified.
3. If a=0 then the function becomes a linear function.
5. If possible, we can use factoring. Otherwise, we can use the quadratic formula.Add texts here.
B: Parabola Orientation
Exercise 3.1e.B
★ Determine if the parabola opens up or down.
|
7. a. f(x)=−2x2−6x−7
8. a. f(x)=4x2+x−4 |
9. a. f(x)=−3x2+5x−1
10. a. f(x)=x2+3x−4 |
11. y=x2−9x+20 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
7. a. down b. up 9. a. down b. up 11. Upward 13. Downward 15. Downward
C: Vertex and Axis of Symmetry
Exercise 3.1e.C
★ Determine the vertex.
|
17. y=−(x−5)2+3 18. y=−2(x−1)2+7 |
19. y=5(x+1)2+6 20. y=3(x+4)2+10 |
21. y=−5(x+8)2−1 22. y=(x+2)2−5 |
★ Find the vertex and the axis of symmetry.
|
23. f(x)=x2+8x−1 24. f(x)=x2+10x+25 25. f(x)=−x2+2x+5 26. f(x)=−2x2−8x−3 |
27. y=−x2+10x−34 28. y=−x2−6x+1 29. y=−4x2+12x−7 30. y=−9x2+6x+2 |
31. y=4x2−1 32. y=x2−16 |
- Answers to Odd Examples
-
17. (5,3)
19. (−1,6)
21. (−8,−1)
23. Vertex: (−4,−17), Axis of symmetry: x=−4
25. Vertex: (1,6), Axis of symmetry: x=1
27. Vertex: (5,−9); axis of symmetry: x=5
29. Vertex: (32,2); axis of symmetry: x=32
31. Vertex: (0,−1); axis of symmetry: x=0
D: Domain and Range
Exercise 3.1e.D
★ Use the vertex of the graph of the quadratic function and the direction the graph opens to find the domain and range of the function.
| 33) Vertex (1,−2), opens up. |
34) Vertex (−1,2) opens down. |
35) Vertex (−5,11), opens down. |
36) Vertex (−100,100), opens up. |
★ Given the following quadratic functions, determine the domain and range.
|
37. f(x)=3x2+30x+50 38. f(x)=5x2−10x+1 39. g(x)=−2x2+4x+1 |
40. g(x)=−7x2−14x−9 41. f(x)=x2+x−1 42. f(x)=−x2+3x−2 |
43) f(x)=(x−3)2+2 44) f(x)=−2(x+3)2−6 45) f(x)=x2+6x+4 |
46) f(x)=2x2−4x+2 47) k(x)=3x2−6x−9
|
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
33. Domain is (−∞,∞). Range is [−2,∞).
35. Domain is (−∞,∞) Range is (−∞,11].
37. Domain: (−∞,∞); range:[−25,∞)
39. Domain: (−∞,∞); range: (−∞,3]
41. Domain: (−∞,∞); range: [−54,∞)
43. Domain is (−∞,∞). Range is [2,∞).
45. Domain is (−∞,∞). Range is [−5,∞).
47. Domain is (−∞,∞). Range is [−12,∞).
E: Minimum or maximum Value
Exercise 3.1e.E
★ In the following exercises, find the maximum or minimum value of each function.
|
49. f(x)=2x2+x−1 50. y=−4x2+12x−5 51. y=x2−6x+15 52. y=−x2+4x−5 53. y=−9x2+16 54. y=4x2−49 |
55. y=−x2−6x+1 56. y=−x2−4x+8 57. y=25x2−10x+5 58. y=16x2−24x+7 59. y=−x2 60. y=1−9x2 |
61. . y=20x−10x2 62. y=12x+4x2 63. y=3x2−4x−2 64. y=6x2−8x+5 65. y=x2−5x+1 66. y=1−x−x2 |
★ Determine whether there is a minimum or maximum value to each quadratic function. Find the value and the axis of symmetry.
|
68. y(x)=2x2+10x+12 69. f(x)=2x2−10x+4 70. f(x)=−x2+4x+3 |
71. f(x)=4x2+x−1 72. h(t)=−4t2+6t−1 |
73) f(x)=12x2+3x+1 74) f(x)=−13x2−2x+3 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
49. The minimum value is −98 when x=−14.
51. The minimum value is 6 when x=3.
53. The maximum value is 16 when x=0.
55. Maximum: y=10
57. Minimum: y=4 when x=15
59. Maximum: y=0
61. Maximum: y=10
63. Minimum: y=−103
65. Minimum: y=−214
69. Minimum is −172 and occurs at 52.
Axis of symmetry is x=52.71. Minimum is −1716 and occurs at −18.
Axis of symmetry is x=−18.73. Minimum is −72 and occurs at −3.
Axis of symmetry is x=−3.
F: Intercepts
Exercise 3.1e.F
★ Determine the x- and y-intercepts of each function.
|
75. f(x)=x2+7x+6 76. f(x)=x2+10x−11 77. f(x)=x2+8x+12 78. f(x)=x2+5x+6 79. f(x)=−x2+8x−19 80. f(x)=−3x2+x−1 81. f(x)=x2+6x+13 82. f(x)=x2+8x+12 |
83. f(x)=4x2−20x+25 84. f(x)=−x2−14x−49 85. f(x)=−x2−6x−9 86. f(x)=4x2+4x+1 87. y=x2+4x−12 88. y=x2−13x+12 89. y=2x2+5x−3 90. y=3x2−4x−4 |
91. y=−5x2−3x+2 92. y=−6x2+11x−4 93. y=4x2−27 94. y=9x2−50 95. y=x2−x+1 96. y=x2−6x+4 97) g(x)=x(x−4)−20 98) g(x)=x(x−2)−10 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
75. y-intercept: (0,6); x-intercept(s): (−1,0),(−6,0)
77. y-intercept: (0,12); x-intercept(s): (−2,0),(−6,0)
79. y-intercept: (0,−19); x-intercept(s): none
81. y-intercept: (0,13); x-intercept(s): none
83. y-intercept: (0,25); x-intercept(s): (52,0)
85. y-intercept: (0,9); x-intercept(s): (−3,0)
87. x-intercepts: (−6,0),(2,0); y-intercept: (0,−12)
89. x-intercepts: (−3,0),(12,0); y-intercept: (0,−3)
91. x-intercepts: (−1,0),(25,0); y-intercept: (0,2)
93. x-intercepts: (−3√32,0),(3√32,0); y-intercept: (0,−27)
95. x-intercepts: none; y-intercept: (0,1)
97. x-intercepts: 2+2√6,2−2√6; y-intercept: (0,−20)
G: Graph Quadratic Functions
Exercise 3.1e.G
★ Sketch a graph of the quadratic function and give the vertex, axis of symmetry, and intercepts.
|
99) f(x)=x2−2x 100) f(x)=x2−6x−1 |
101) f(x)=x2−5x−6 102) f(x)=x2−7x+3 |
103) f(x)=−2x2+5x−8
|
105) f(x)=4x2−12x−3
|
★ Sketch each quadratic function below
|
107. f(x)=x2−10x 108. f(x)=x2+8x 109. f(x)=x2−9 110. f(x)=x2−25 |
111. f(x)=1−x2 112. f(x)=4−x2 113. f(x)=x2−2 114. f(x)=x2−3 |
115. f(x)=−2x2+3 116. f(x)=−2x2−1 117. f(x)=x2−1 118. f(x)=x2+1 |
121. n/a 122. f(x)=13x2−3 123. n/a 124. f(x)=5x2+2 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
99.

Vertex (1,−1),
Axis of symmetry is x=1.
Intercepts: (0,0),(2,0)101.

Vertex (52,−494),
Axis of symmetry is x=52.
Intercepts: (0,−6),(−1,0),(6,0)103.

Vertex (54,−398),
Axis of symmetry is x=54.
Intercepts: (0,−8)105.

Vertex (32,−12),
Axis of symmetry is x=32,
Intercepts: (32±√3,0), (0,−3)107.
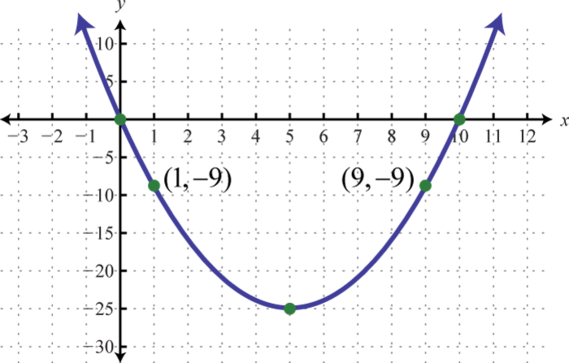
Figure 107 109.
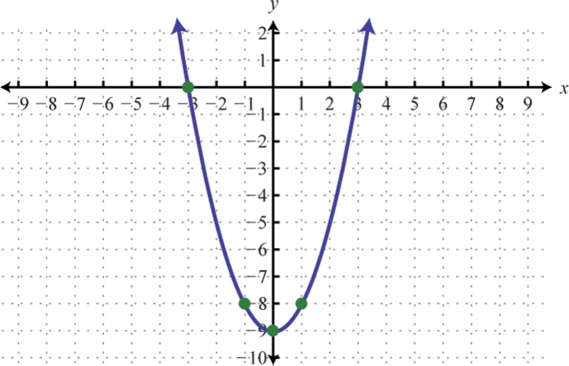
Figure 109 111.
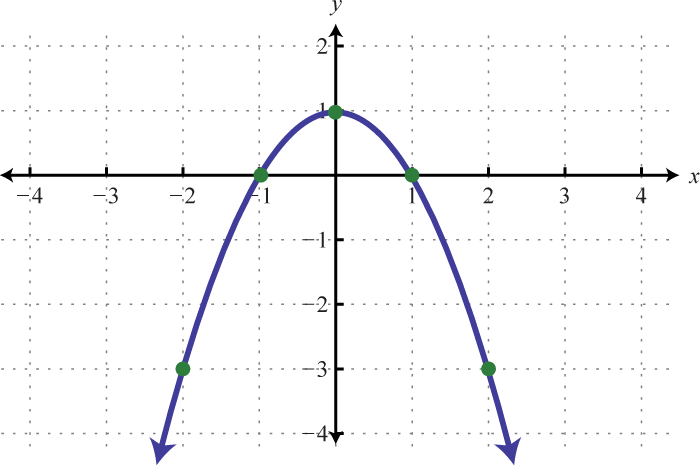
Figure 111 113.
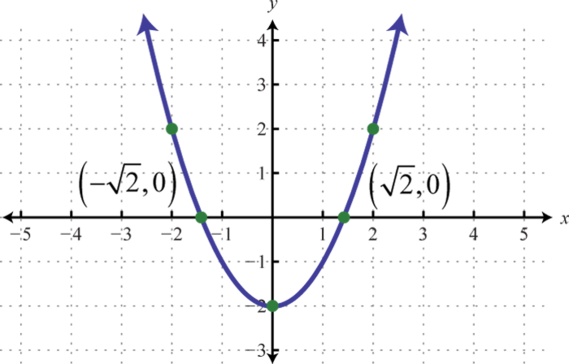
Figure 113 115.
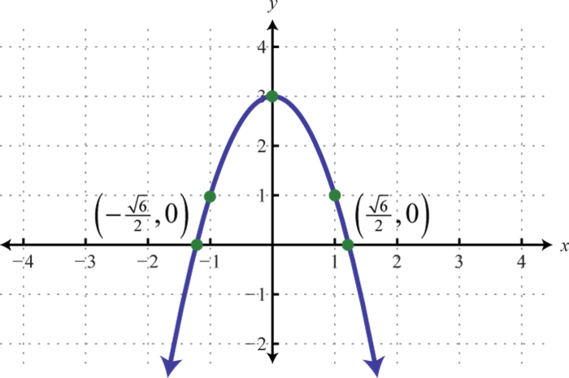
Figure 115 117.
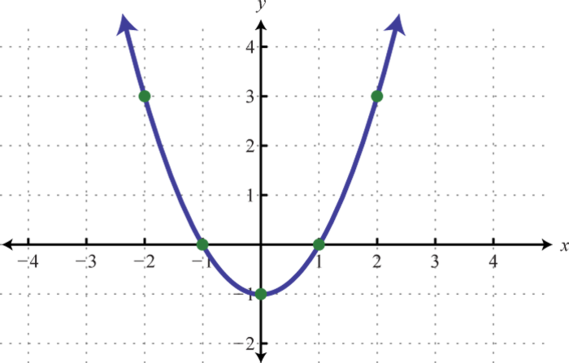
Figure 117
★ Sketch each quadratic function below
|
125. f(x)=−x2+2x−7 126. f(x)=−x2+2x−4 127. f(x)=x2−2x−8 128. f(x)=−x2−2x+15 |
129. f(x)=x2+3x+4 130. f(x)=−x2+3x−4 131. f(x)=x2+4x+3 132. f(x)=x2+4x−12 |
133. f(x)=−x2−4x+2 134. f(x)=−x2+4x−5 135. f(x)=x2+6x+5 136. f(x)=x2−6x+8 |
137. f(x)=x2−6x+15 138. f(x)=x2−6x+6 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
125.

Figure 125 127.
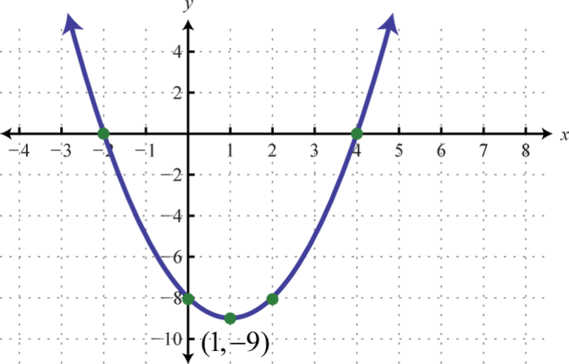
Figure 127 133.

Figure 133 129.
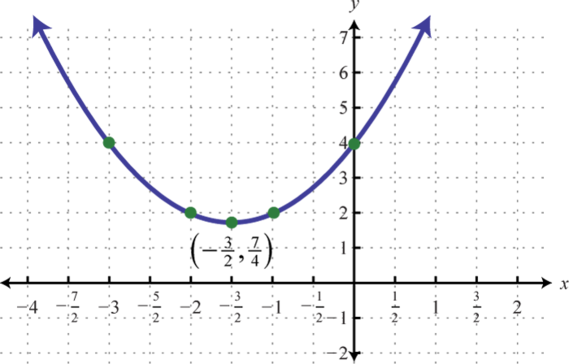
Figure 129 135.

Figure 135 131.

Figure 133 137.

Figure 137
★ Sketch each quadratic function below
|
145. f(x)=2x2−4x+1 146. f(x)=3x2−6x−1 147. f(x)=−2x2+8x−10 148. f(x)=−2x2−4x−5 149. f(x)=5x2−10x+8 150. f(x)=3x2−12x+7 |
151. f(x)=3x2+18x+20 152. f(x)=−3x2+6x+1 153. f(x)=−4x2+12x−9 154. f(x)=−4x2−6x−2 155. f(x)=−4x2+4x−3 156. f(x)=−4x2−4x+3 |
157. f(x)=−2x2+6x−3 158. f(x)=9x2+12x+4 159. f(x)=2x2+4x−3 160. f(x)=3x2+2x−2 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
145.

Figure 145 147.

Figure 147 149.

Figure 149 151.

Figure 151 153.
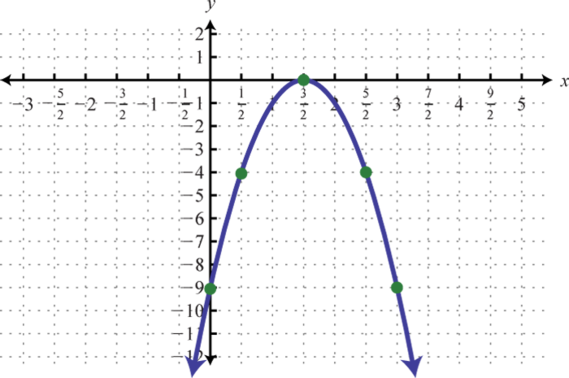
Figure 153 155.
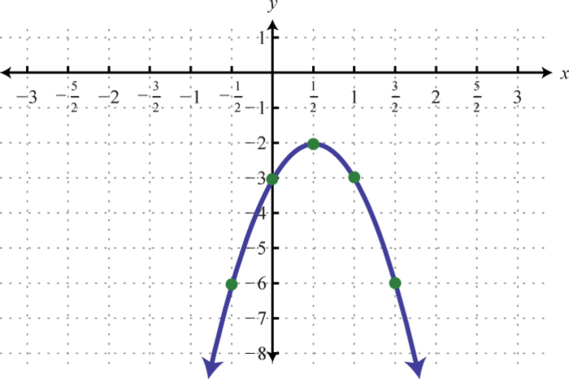
Figure 155 157.
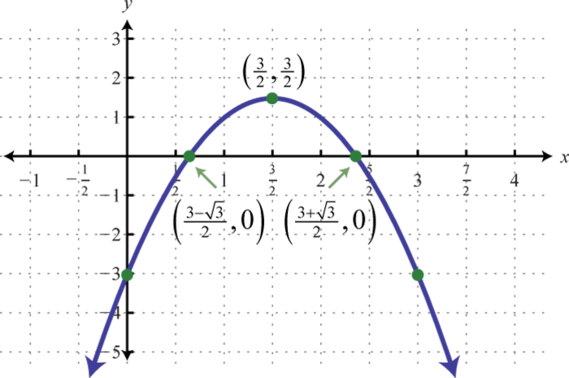
Figure 157 159.
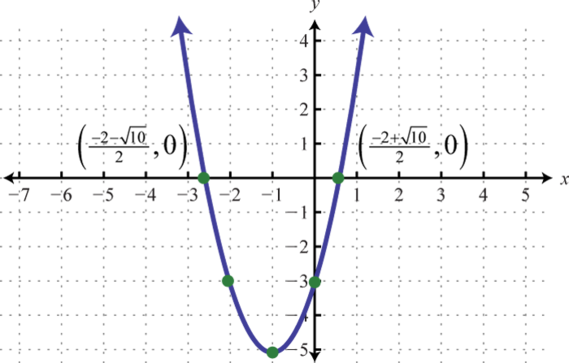
Figure 117
★ Sketch each quadratic function below
|
165. f(x)=(x−1)2 166. f(x)=(x+1)2 167. f(x)=(x−1)2+5 169. f(x)=(x−3)2+4 169. f(x)=(x−4)2−9 170. f(x)=(x−6)2−2 |
171. f(x)=(x+2)2+1 172. f(x)=(x+3)2−1 173. f(x)=(x−4)2−3 174. f(x)=(x+5)2−2 175. f(x)=−2(x−4)2+22 176. f(x)=2(x+3)2−13 |
177. f(x)=−2(x+1)2+8 178. f(x)=−2(x−5)2−3 179. f(x)=−4(x−1)2−2 180. f(x)=−3(x+2)2+12 181. f(x)=−5(x−1)2 182. f(x)=−(x+2)2 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
165.
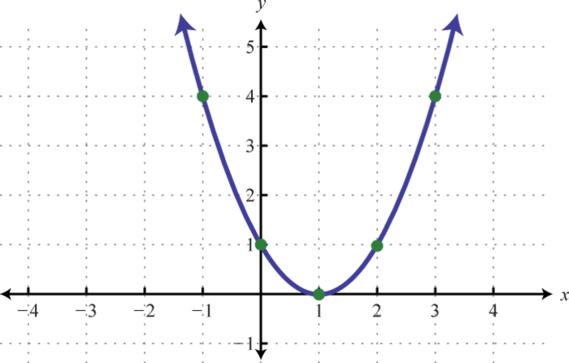
Figure 165 167.

Figure 167 169.
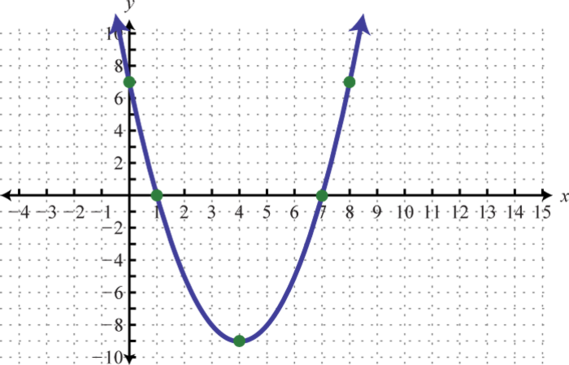
Figure 169 171.

Figure 171 173.

Figure 173 175.
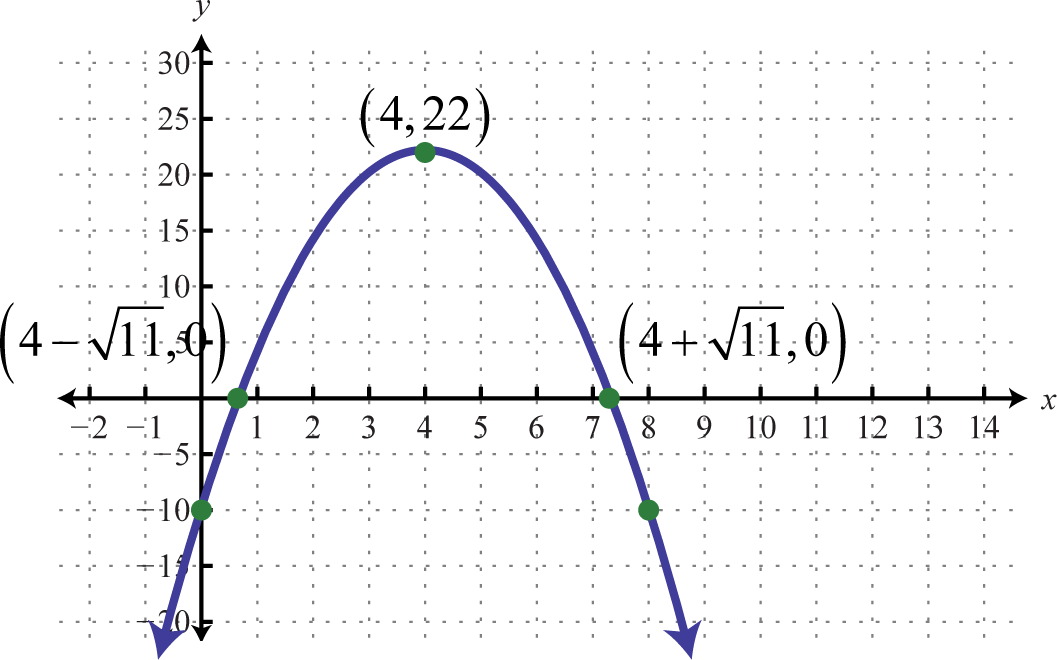
Figure 175 177.
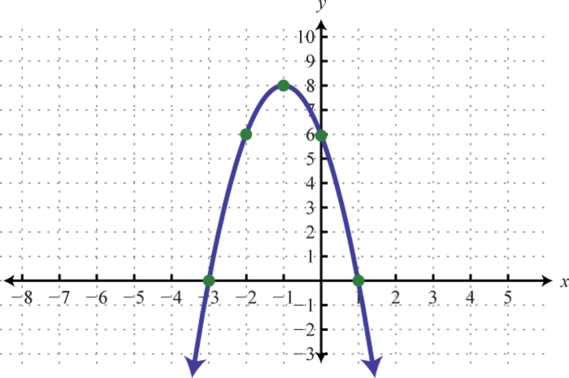
Figure 177 179.
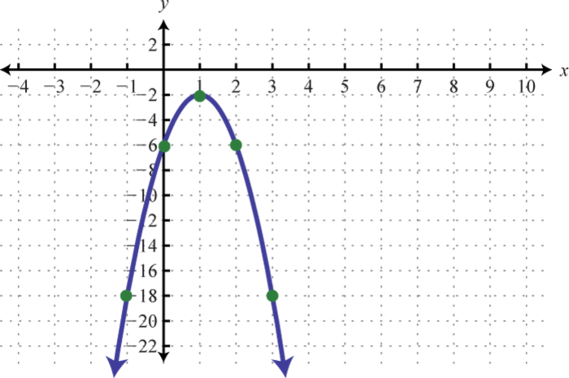
Figure 179 181.
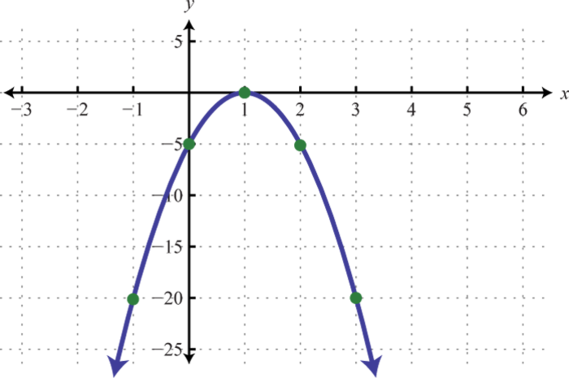
Figure 181
H: Convert to vertex form
Exercise 3.1e.H
★ Rewrite in Standard (vertex) form y=a(x−h)2+k and determine the vertex.
|
185. y=x2−14x+24 186. y=x2−12x+40 187. y=x2+4x−12 188. y=x2+6x−1 189. y=2x2−12x−3 190. y=3x2−6x+5 191. y=−x2+16x+17 192. y=−x2+10x |
193. f(x)=−x2−4x+2 194. f(x)=x2−12x+32 195. g(x)=x2+2x−3 196. f(x)=x2−x 197. f(x)=x2+5x−2 198. h(x)=2x2+8x−10 199. k(x)=3x2−6x−9 200. f(x)=2x2−6x |
201. f(x)=3x2−5x−1 203. f(x)=−3x2−12x−5 204. f(x)=2x2−12x+7 205. f(x)=3x2+6x−1 206. f(x)=−4x2−16x−9 207. f(x)=5x2−10x+8 208. f(x)=3x2−6x−1 209. f(x)=2x2−4x+1 210. f(x)=−16x2+24x+6 |
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
185. y=(x−7)2−25; vertex: (7,−25)
187. y=(x+2)2−16; vertex: (−2,−16)
189. y=2(x−3)2−21; vertex: (3,−21)
191. y=−(x−8)2+81; vertex: (8,81)
193. f(x)=−(x+2)2+6; vertex: (−2,6)
195. g(x)=(x+1)2−4, Vertex (−1,−4)
197. f(x)=(x+52)2−334, Vertex (−52,−334)
199. k(x)=3(x−1)2−12, Vertex (1,−12)
201. f(x)=3(x−56)2−3712, Vertex (56,−3712)
203. f(x)=−3(x+2)2+7; vertex: (−2,7)
205. f(x)=3(x+1)2−4; vertex: (−1,−4)
207. f(x)=5(x−1)2+3; vertex: (1,3)
209. f(x)=2(x−1)2−1; vertex: (1,−1)
I: Convert to vertex form
Exercise 3.1e.I
★ In the following exercises, write the quadratic function in f(x)=a(x−h)2+k form whose graph is shown.
|
211. |
212. |
213. |
214. |
|
215.
|
216.
|
217.
|
218.
|
|
219.
|
220.
|
221.
|
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
211. f(x)=(x+1)2−5
213. f(x)=2(x−1)2−3
215. f(x)=x2−4x+1
217. f(x)=−2x2+8x−1
219. f(x)=12x2−3x+72
221. f(x)=−(x−4)2+0
J: Construct an equation from points
Exercise 3.1e.J
★ Use the vertex (h,k) and a point on the graph (x,y) to find the general form of the equation of the quadratic function.
|
223) (h,k)=(2,0),(x,y)=(4,4) 224) (h,k)=(−2,−1),(x,y)=(−4,3) 225) (h,k)=(0,1),(x,y)=(2,5) 226) (h,k)=(2,3),(x,y)=(5,12) |
227) (h,k)=(−5,3),(x,y)=(2,9) 228) (h,k)=(3,2),(x,y)=(10,1) 229) (h,k)=(0,1),(x,y)=(1,0) 230) (h,k)=(1,0),(x,y)=(0,1) |
★ Write the equation of the quadratic function that contains the given point and has the same shape as the given function.
231) Contains (1,1) and has shape of f(x)=2x2. Vertex is on the y-axis.
232) Contains (−1,4) and has the shape of f(x)=2x2. Vertex is on the y-axis.
233) Contains (2,3) and has the shape of f(x)=3x2. Vertex is on the y-axis.
234) Contains (1,−3) and has the shape of f(x)=−x2. Vertex is on the y-axis.
235) Contains (4,3) and has the shape of f(x)=5x2. Vertex is on the y-axis.
236) Contains (1,−6) has the shape of f(x)=3x2. Vertex has x-coordinate of −1.
- Answers to Odd Examples:
-
223. f(x)=x2−4x+4
225. f(x)=x2+1
227. f(x)=649x2+6049x+29749
229. f(x)=−x2+1
231. f(x)=2x2−1
233. f(x)=3x2−9
235. f(x)=5x2−77












